
HeyMoe
Leveraging virtual robot and game mechanics to mobile prototype application design for Chinese language learning
Introduction:
With the growth of internet technology, individuals currently enjoy a better experience in using interactive systems like desktop computer software or mobile device applications than before in their lives. Moreover, using mobile phones in learning activities is also becoming increasingly more popular in these years. However, the learning applications today do not fully meet the learner’s needs, especially young adults who have some interest and do not have any fundamental knowledge in their study subjects. Combining AI technology and game elements could make it possible to solve this problem.
In this way, the location limitations and boringness of the learning activities could be efficiently reduced. This study presents an idea of applying virtual robot and game elements to language learning activity and creating a mobile device application prototype to enhances the learner’s Chinese study experience.
Thesis Committee:
Adam Smith
Joyce Hertzson
Chris Jackson
Student:
Boxiao Gong
Platform:
Mobile Device
Problem:
Today, the role of the educational process becomes more challenging and learning environments, such as classrooms or museums in their traditional form, fail to engage and motivate students. Many instructors in the field of education using the conventional teaching methods are facing this kind of problems with student nowadays.
The reason for this is the process of the traditional learning method are mostly reading textbooks or attending lectures, which seems to make Chinese learning difficult to English-speaking students and missing opportunities to leverage technology and online resources.
Why learning Chinese:
955 million
There are over 955 million native Mandarin Chinese speakers worldwide. This fact means that by learning Chinese, you unlock the potential to speak to over 13% of the world’s total population. (Sean McGibney. 2015)
Unlock a different part of your brain
Studies suggest that people who speak Chinese will learn to use both temporal lobes of their mind, whereas English speakers will only use the left side. Both temporal lobes are required to distinguish between words that have different intonation in Mandarin. (Sean McGibney. 2015)
Methods:
AI-powered robot tutor
- Learning and traveling with the users
- Facial experssion display in the learning process
- Cute and be welcome to the users
Location-based recommendation
- Detect and understand the user’s location
- Create Chinese word cards and word challenges relating to the location
Life-like conversation study
- Based on the location users went, generates conversation and word study courses
- Develop user's daily life Chinese speaking abilities
Game components
- The Achievement component
- The Challenge component
- The Immersion component
Approach and Objectives:
Many American students nowadays are learning Chinese as a second language.
For example, in RIT, there are three classes in Chinese language learning program, and each class have about 30 students. Moreover, the author have experience teaching Chinese in Canada. The author found that many North American students have interest in learning Chinese, but because Chinese and English are from different language family, and Chinese is not their required course, so many of them give up easily during the semesters.
This project aims to develop a solution to increase the students experience in learning Chinese language by designing a mobile device application prototype. The four major objectives of Moe are:
1. Creating an emotional robot to help users to learn anytime and anywhere
2. Applying game components to the app for increasing user's motivation during the language learning process
3. Filling user's free time with location-based recommendation and word card design
4. Practicing life-like conversations in the app to improve user's speaking abilities
User studies:
The target audience of the application is America college students with an age range between eighteen to twenty-five and twenty-six to sixty. Gender of the users can be both Male and female. The user’s education level has primary speaking and reading skills. User’s range could be from ordinary people who want to get a little taste of what Chinese language. Moreover, it could also be the second generation of immigrants from China as well as International travelers who like China a lot.
The most valuable personas are based on observing real individuals. Based on the target user, below are two personas for this project:


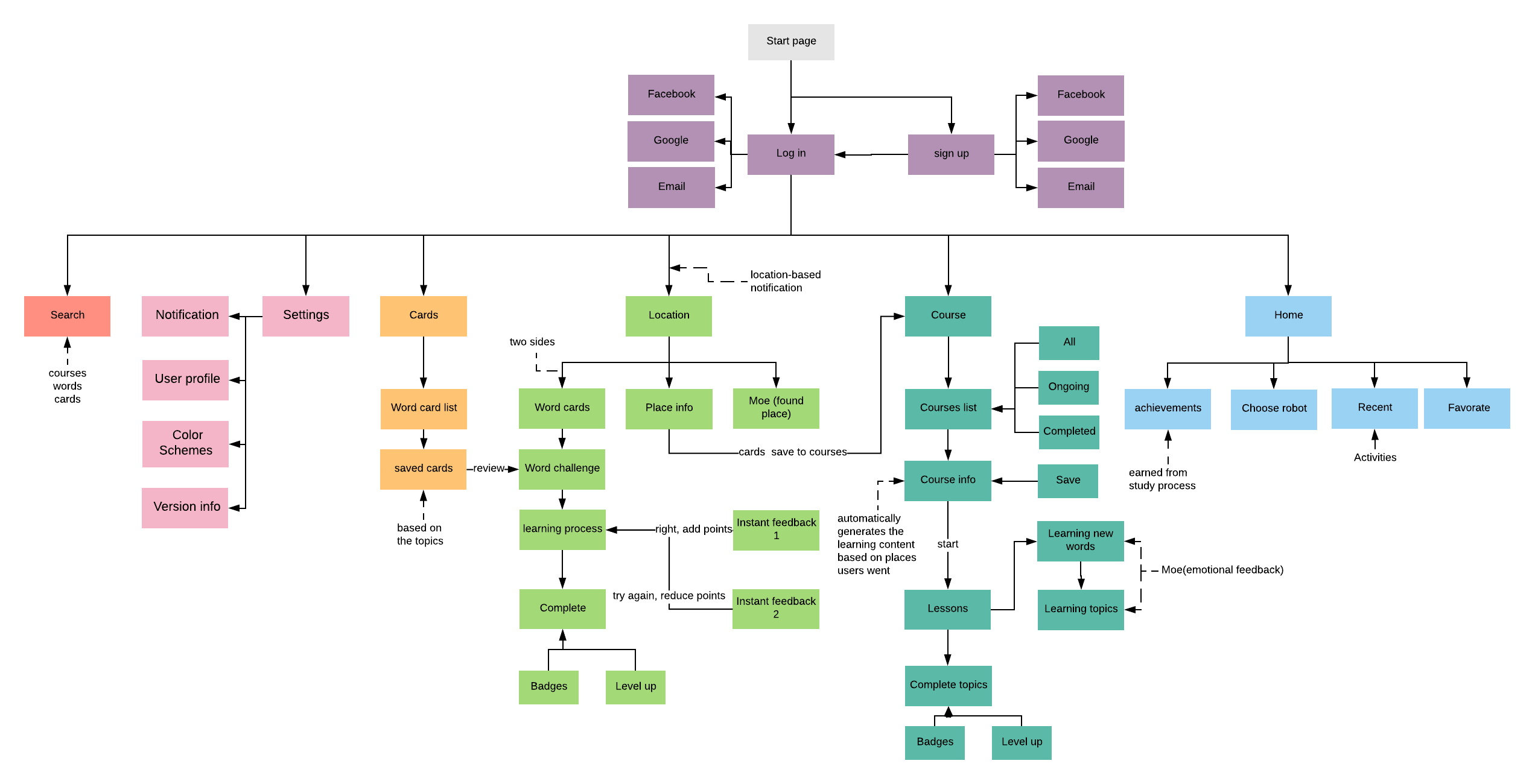
Information Architecture:
The development of the application’s Information Architecture is aim to indicates the workflows of application. To make it easy to understand, the author used a color-coding method to represent different sections.
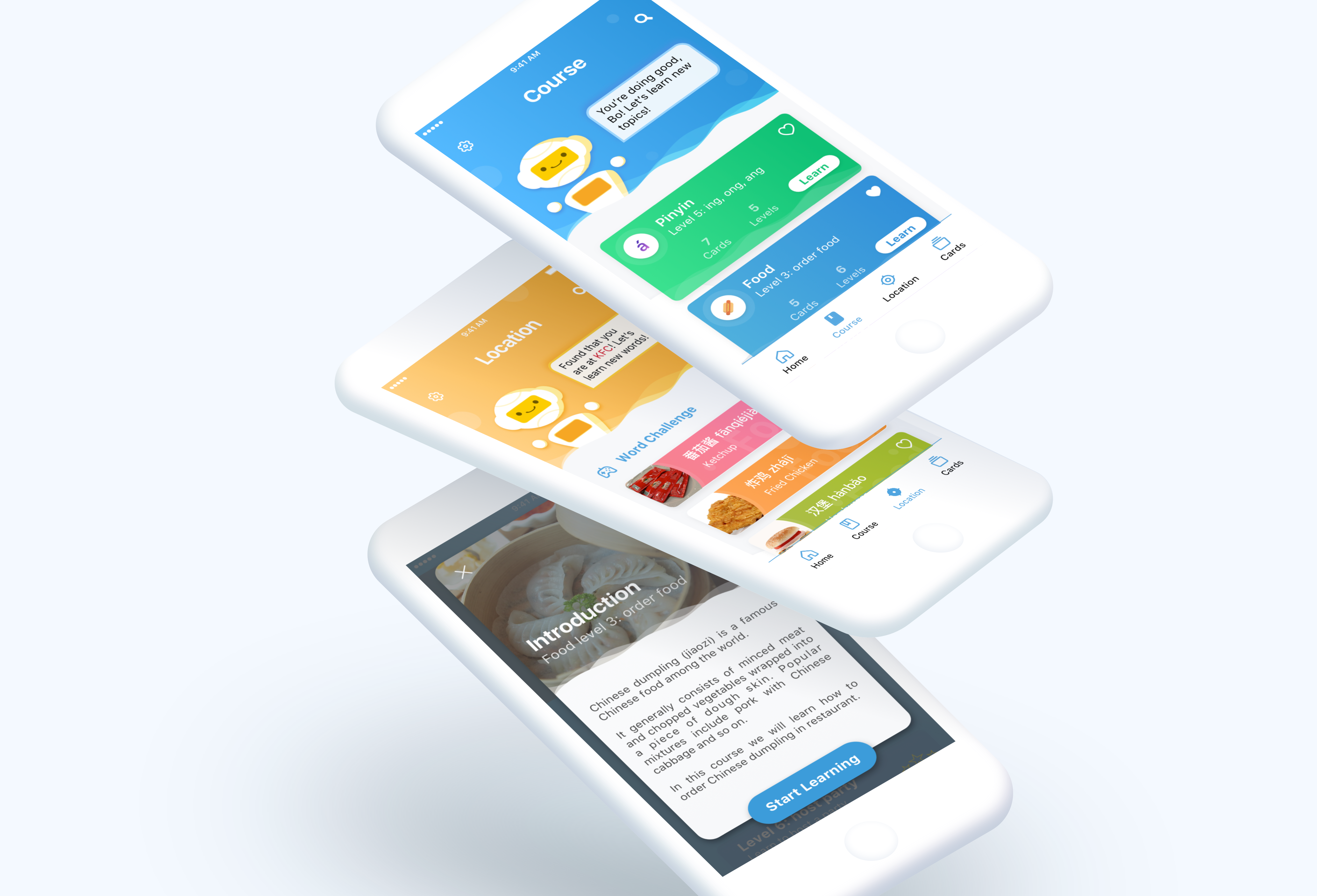
Course study:
Fluency in a language is not only how many words you know, but how well you communicate with the words you do. (Ergürel. 2017) This learning mode focus on the life-like Chinese speaking practice as well as culture introduction. The application automatically generates learning contents based the places they went. The courses would give users necessary Chinese language skills to communicate with people in those places.
- During the study, users can listen and learn words and conversation, and Moe will detect the answers by voice.
- Users will earn points if they answer right, and lose points when they answered wrong.
- After user completed the level, there will be a complete page. It could also show that user has upgraded to a new level or earned a badge.
Location-based recommendation:
Based on the fast-paced nature of the age of the internet today, this study mode aims to teach learners location-based words quickly by cards and word challenges with Moe. In this mode, the application automatically detects the location and make recommendations of the Chinese words related to the place.
- Word cards: Auto generates word card list based on the location that users at.
- Word challenge: multiple types questions and quizzes.
- Instant feedback: tells users they answered right or wrong. The point will be added or lost based on the answers.
- Save card: users could save the words.
Homepage:
In the home page, users could access to learning contents as well as checking their progress. Moreover, there are other functions: From the icons below, users could check the places they went, words they have learned and select Robot they like to study with.
- Check progress: By clicking the top card, users could check their learning progress and see what achievement they have got so far.
- Course topics: users could click the topic icons to go to course learning sections.

Thank you
Selected Works

XiHe-LONE-International Social Shopping SolutionCase Study 1-page

Yushinanshan-Protect Me - DuplicateCase Study 1-page

KATHY JIANG-SOLO DINERCase Study 1-page

Akshay Kumar Arun - Authentic Travel Leveraging Local Social MediaCase Study 1-page

Ding - Smart Tracking for Healthier LifestyleCase Study 1-page
I-Tang, Wu_Additives AbyssCase Study 1-page

Art Museums and Early ChildhoodCase Study

WENTAO HUANG_MudboyCase Study 1-page

Ying - Adopt MeCase Study 1-page

LIU- Rover (Virtual Reality Game)Case Study 1-page
Hou - You Can Be StrongCase Study 1-page

Jing Lyu - VR Interactive Prototype: Future WardrobeCase Study 1-page

Huangzhi Tang - ID ( Ego & Id )Experimental Animation
VATANASIRISUK - History of The WorldCase Study 1-page

Lopez Taveras – Virtual Reality Interfaces for Product DesignInteraction Design

Zheng Zhang - Sense - A recommendation SystemCase Study 1-page

Zhan - Skin health improvement appCase study- 1page

Chenchen Ji - CatpanionCase Study 1-page

XU-Educational tool to prevent injuries from outdoor adventuresCase Study 1-page

